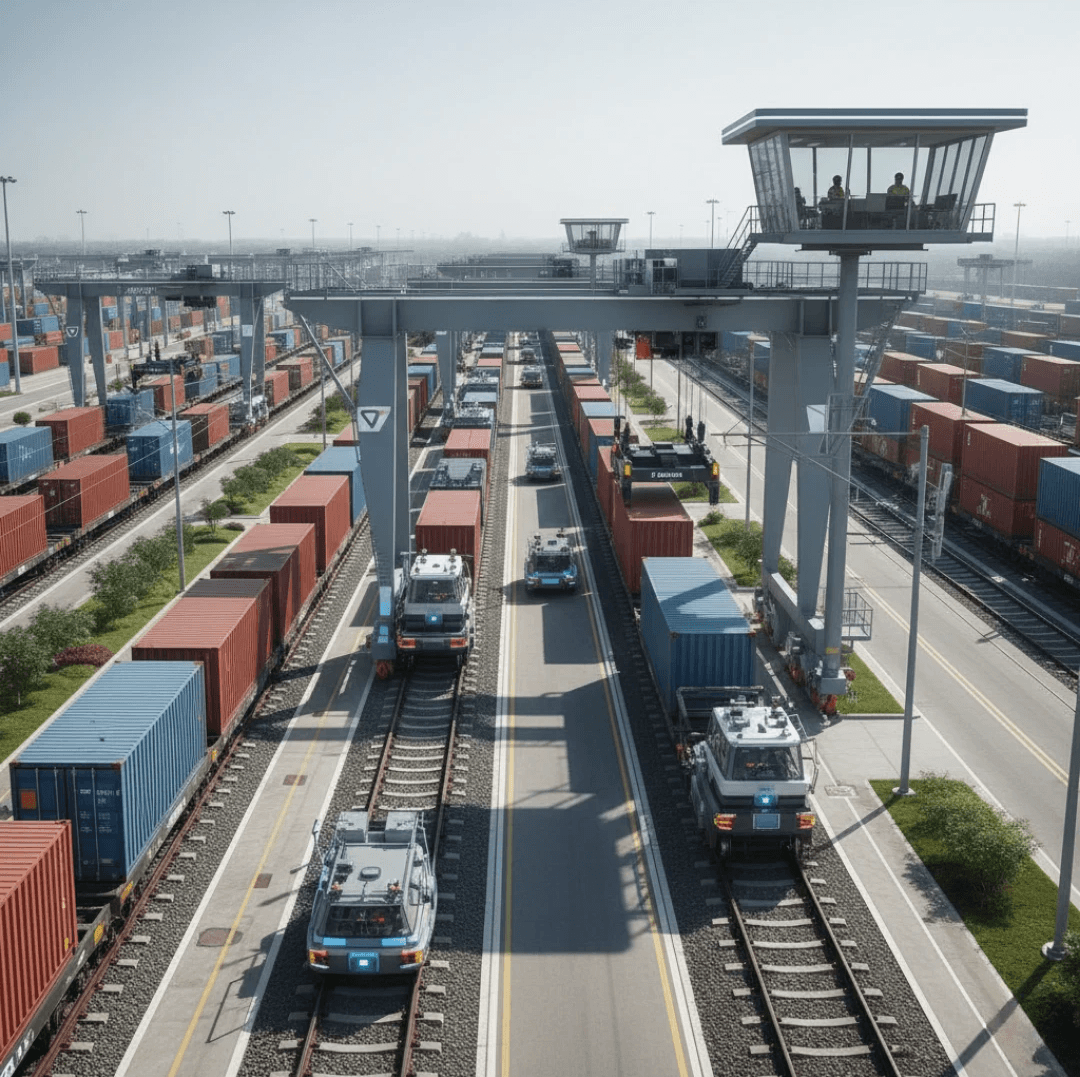
BLOG DETAILS
BLOG DETAILS
BLOG DETAILS
Sustainable Infrastructure Innovation: Aligning Industrial Growth with Environmental Responsibility
Sustainable Infrastructure Innovation: Aligning Industrial Growth with Environmental Responsibility
Sustainable Infrastructure Innovation: Aligning Industrial Growth with Environmental Responsibility
Feb 7, 2026
/
savik infra
/
12 min
Feb 7, 2026
/
savik infra
/
12 min
Feb 7, 2026
/
savik infra
/
12 min




Introduction: The Shift Toward Sustainable Infrastructure in India
India’s industrial expansion is accelerating, driven by manufacturing growth, freight modernization, and large-scale infrastructure investment. However, alongside economic progress comes the responsibility of environmental stewardship. Sustainable infrastructure innovation in India is emerging as the defining factor that will balance industrial growth with ecological responsibility.
Today, infrastructure developers are not only evaluated on execution speed and project scale but also on environmental impact, carbon footprint reduction, and long-term sustainability. Organizations collaborating with national institutions such as Indian Railways are increasingly integrating green practices into railway infrastructure, freight corridors, and industrial connectivity projects.
Sustainability is no longer a compliance checkbox—it is a strategic imperative for future-ready infrastructure.
Understanding Sustainable Infrastructure Innovation
Sustainable infrastructure innovation refers to the design, construction, and operation of infrastructure assets that minimize environmental impact while maximizing long-term economic and social value. In industrial logistics and railway development, this includes energy-efficient systems, renewable energy integration, optimized land use, water conservation, and emission reduction strategies.
Modern railway siding projects and freight terminals are being planned with improved drainage systems, dust control mechanisms, electrified rail operations, and solar-powered facilities. Electrification initiatives across India’s rail network significantly reduce diesel dependency, supporting national climate objectives.
For infrastructure companies, adopting sustainable engineering practices enhances operational efficiency while aligning with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) standards.
Introduction: The Shift Toward Sustainable Infrastructure in India
India’s industrial expansion is accelerating, driven by manufacturing growth, freight modernization, and large-scale infrastructure investment. However, alongside economic progress comes the responsibility of environmental stewardship. Sustainable infrastructure innovation in India is emerging as the defining factor that will balance industrial growth with ecological responsibility.
Today, infrastructure developers are not only evaluated on execution speed and project scale but also on environmental impact, carbon footprint reduction, and long-term sustainability. Organizations collaborating with national institutions such as Indian Railways are increasingly integrating green practices into railway infrastructure, freight corridors, and industrial connectivity projects.
Sustainability is no longer a compliance checkbox—it is a strategic imperative for future-ready infrastructure.
Understanding Sustainable Infrastructure Innovation
Sustainable infrastructure innovation refers to the design, construction, and operation of infrastructure assets that minimize environmental impact while maximizing long-term economic and social value. In industrial logistics and railway development, this includes energy-efficient systems, renewable energy integration, optimized land use, water conservation, and emission reduction strategies.
Modern railway siding projects and freight terminals are being planned with improved drainage systems, dust control mechanisms, electrified rail operations, and solar-powered facilities. Electrification initiatives across India’s rail network significantly reduce diesel dependency, supporting national climate objectives.
For infrastructure companies, adopting sustainable engineering practices enhances operational efficiency while aligning with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) standards.
Introduction: The Shift Toward Sustainable Infrastructure in India
India’s industrial expansion is accelerating, driven by manufacturing growth, freight modernization, and large-scale infrastructure investment. However, alongside economic progress comes the responsibility of environmental stewardship. Sustainable infrastructure innovation in India is emerging as the defining factor that will balance industrial growth with ecological responsibility.
Today, infrastructure developers are not only evaluated on execution speed and project scale but also on environmental impact, carbon footprint reduction, and long-term sustainability. Organizations collaborating with national institutions such as Indian Railways are increasingly integrating green practices into railway infrastructure, freight corridors, and industrial connectivity projects.
Sustainability is no longer a compliance checkbox—it is a strategic imperative for future-ready infrastructure.
Understanding Sustainable Infrastructure Innovation
Sustainable infrastructure innovation refers to the design, construction, and operation of infrastructure assets that minimize environmental impact while maximizing long-term economic and social value. In industrial logistics and railway development, this includes energy-efficient systems, renewable energy integration, optimized land use, water conservation, and emission reduction strategies.
Modern railway siding projects and freight terminals are being planned with improved drainage systems, dust control mechanisms, electrified rail operations, and solar-powered facilities. Electrification initiatives across India’s rail network significantly reduce diesel dependency, supporting national climate objectives.
For infrastructure companies, adopting sustainable engineering practices enhances operational efficiency while aligning with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) standards.
Building home, happy hearts
Building home, happy hearts
Innovative technology with building better development
Innovative technology with building better development
Discovering possibility and transparent communication
Discovering possibility and transparent communication
The ability to turnaround costing with sustainable construction
The ability to turnaround costing with sustainable construction
Building home, happy hearts
Innovative technology with building better development
Discovering possibility and transparent communication
The ability to turnaround costing with sustainable construction
Building home, happy hearts
Innovative technology with building better development
Discovering possibility and transparent communication
The ability to turnaround costing with sustainable construction
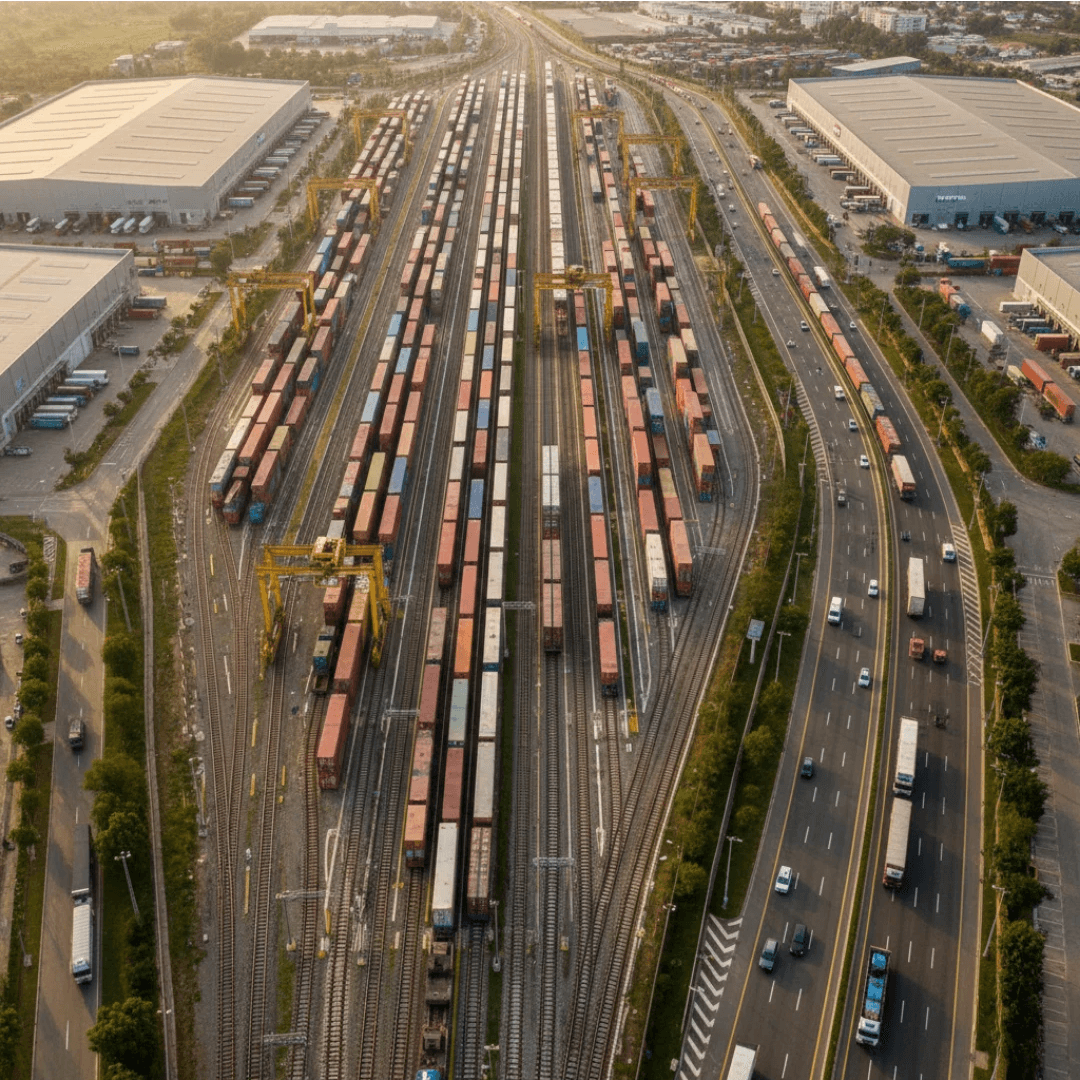
Rail-Based Logistics & Carbon Reduction
Rail transport is inherently more energy-efficient than road freight for long-distance and bulk cargo movement. By promoting rail-based logistics solutions and multimodal integration, India is reducing its logistics-related carbon emissions.
The expansion of freight corridors under the Dedicated Freight Corridor Corporation of India Limited is not only improving cargo efficiency but also supporting sustainable freight movement. Electrified corridors enable faster, cleaner transportation with reduced fuel consumption.
Private railway siding development further strengthens this sustainable shift. Direct rail connectivity to industrial facilities reduces truck traffic, lowers fuel usage, and minimizes urban congestion—contributing to cleaner air and improved environmental performance.
Green Construction Practices in Infrastructure Development
Sustainability begins at the construction stage. Infrastructure developers are increasingly incorporating eco-friendly materials, optimized concrete usage, recycled aggregates, and energy-efficient construction equipment into project execution.
Advanced planning tools help minimize land disturbance and protect natural ecosystems during railway and industrial infrastructure development. Water management systems, including rainwater harvesting and controlled drainage, reduce environmental stress in industrial zones.
By integrating sustainability into project design and engineering, infrastructure companies create long-term assets that operate efficiently while minimizing ecological disruption.
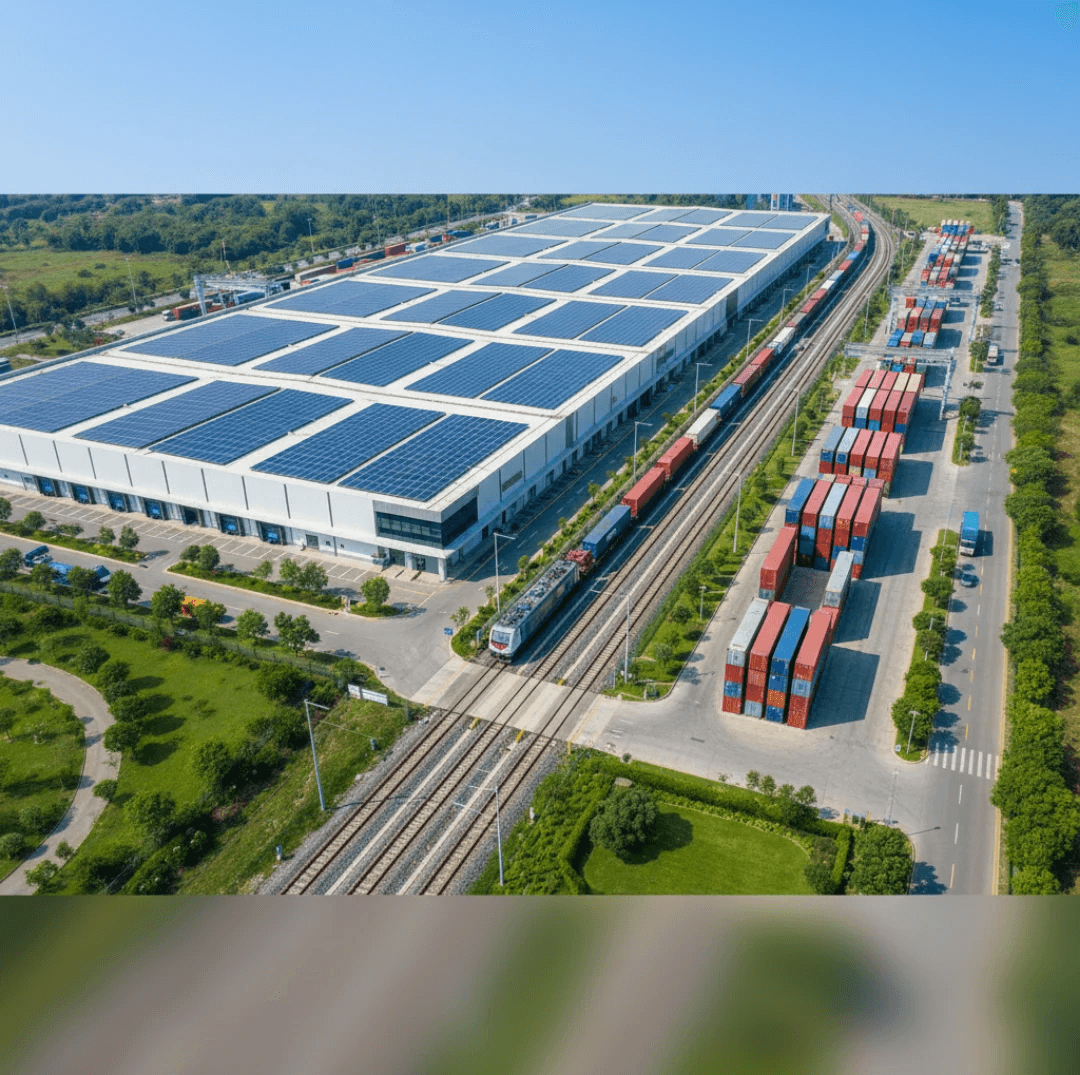
Renewable Energy Integration in Industrial Infrastructure
The integration of renewable energy solutions is transforming India’s infrastructure landscape. Solar panels installed at railway stations, logistics hubs, and industrial warehouses reduce dependency on conventional energy sources. Rooftop solar systems and energy-efficient lighting systems are becoming standard in modern infrastructure projects.
Rail electrification efforts led by Indian Railways further reinforce this transition toward sustainable mobility. Electrified rail networks not only enhance operational efficiency but also reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
For infrastructure developers, renewable energy integration is both an environmental responsibility and a cost-optimization strategy over the long term.

Rail-Based Logistics & Carbon Reduction
Rail transport is inherently more energy-efficient than road freight for long-distance and bulk cargo movement. By promoting rail-based logistics solutions and multimodal integration, India is reducing its logistics-related carbon emissions.
The expansion of freight corridors under the Dedicated Freight Corridor Corporation of India Limited is not only improving cargo efficiency but also supporting sustainable freight movement. Electrified corridors enable faster, cleaner transportation with reduced fuel consumption.
Private railway siding development further strengthens this sustainable shift. Direct rail connectivity to industrial facilities reduces truck traffic, lowers fuel usage, and minimizes urban congestion—contributing to cleaner air and improved environmental performance.
Green Construction Practices in Infrastructure Development
Sustainability begins at the construction stage. Infrastructure developers are increasingly incorporating eco-friendly materials, optimized concrete usage, recycled aggregates, and energy-efficient construction equipment into project execution.
Advanced planning tools help minimize land disturbance and protect natural ecosystems during railway and industrial infrastructure development. Water management systems, including rainwater harvesting and controlled drainage, reduce environmental stress in industrial zones.
By integrating sustainability into project design and engineering, infrastructure companies create long-term assets that operate efficiently while minimizing ecological disruption.
Renewable Energy Integration in Industrial Infrastructure
The integration of renewable energy solutions is transforming India’s infrastructure landscape. Solar panels installed at railway stations, logistics hubs, and industrial warehouses reduce dependency on conventional energy sources. Rooftop solar systems and energy-efficient lighting systems are becoming standard in modern infrastructure projects.
Rail electrification efforts led by Indian Railways further reinforce this transition toward sustainable mobility. Electrified rail networks not only enhance operational efficiency but also reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
For infrastructure developers, renewable energy integration is both an environmental responsibility and a cost-optimization strategy over the long term.

Rail-Based Logistics & Carbon Reduction
Rail transport is inherently more energy-efficient than road freight for long-distance and bulk cargo movement. By promoting rail-based logistics solutions and multimodal integration, India is reducing its logistics-related carbon emissions.
The expansion of freight corridors under the Dedicated Freight Corridor Corporation of India Limited is not only improving cargo efficiency but also supporting sustainable freight movement. Electrified corridors enable faster, cleaner transportation with reduced fuel consumption.
Private railway siding development further strengthens this sustainable shift. Direct rail connectivity to industrial facilities reduces truck traffic, lowers fuel usage, and minimizes urban congestion—contributing to cleaner air and improved environmental performance.
Green Construction Practices in Infrastructure Development
Sustainability begins at the construction stage. Infrastructure developers are increasingly incorporating eco-friendly materials, optimized concrete usage, recycled aggregates, and energy-efficient construction equipment into project execution.
Advanced planning tools help minimize land disturbance and protect natural ecosystems during railway and industrial infrastructure development. Water management systems, including rainwater harvesting and controlled drainage, reduce environmental stress in industrial zones.
By integrating sustainability into project design and engineering, infrastructure companies create long-term assets that operate efficiently while minimizing ecological disruption.
Renewable Energy Integration in Industrial Infrastructure
The integration of renewable energy solutions is transforming India’s infrastructure landscape. Solar panels installed at railway stations, logistics hubs, and industrial warehouses reduce dependency on conventional energy sources. Rooftop solar systems and energy-efficient lighting systems are becoming standard in modern infrastructure projects.
Rail electrification efforts led by Indian Railways further reinforce this transition toward sustainable mobility. Electrified rail networks not only enhance operational efficiency but also reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
For infrastructure developers, renewable energy integration is both an environmental responsibility and a cost-optimization strategy over the long term.

India’s industrial expansion is accelerating, driven by manufacturing growth, freight modernization, and large-scale infrastructure investment.
India’s industrial expansion is accelerating, driven by manufacturing growth, freight modernization, and large-scale infrastructure investment.
India’s industrial expansion is accelerating, driven by manufacturing growth, freight modernization, and large-scale infrastructure investment.
India’s industrial expansion is accelerating, driven by manufacturing growth, freight modernization, and large-scale infrastructure investment.
ESG Compliance & Long-Term Industrial Resilience
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) frameworks are now central to infrastructure investment decisions. Investors and stakeholders increasingly evaluate projects based on sustainability performance, carbon management, and social impact.
By adopting green infrastructure practices, companies strengthen investor confidence and improve regulatory compliance. Sustainable projects are more resilient to future environmental regulations and climate-related risks.
Aligning infrastructure development with ESG principles ensures that industrial expansion does not compromise environmental integrity or community well-being.
The Future of Sustainable Infrastructure in India
India’s path toward becoming a global manufacturing and logistics hub depends on building infrastructure that is both robust and environmentally responsible. Continued rail electrification, renewable energy adoption, multimodal integration, and green construction standards will define the next phase of infrastructure growth.
As industrial output rises, sustainable logistics solutions will become critical to balancing economic expansion with environmental conservation. Infrastructure innovation must therefore focus on efficiency, reduced emissions, and intelligent resource management.
Developers who integrate sustainability into every phase—from planning and design to construction and operation—will lead India’s transition toward a greener industrial future.
Conclusion
Sustainable infrastructure innovation is reshaping the way India approaches industrial growth. By aligning railway development, logistics integration, renewable energy adoption, and green construction practices, the nation is building an infrastructure ecosystem that supports both economic progress and environmental responsibility.
For infrastructure leaders, sustainability is not a constraint—it is a competitive advantage. Forward-thinking organizations that prioritize eco-friendly engineering and ESG compliance will play a central role in strengthening India’s industrial backbone while safeguarding its environmental future.
ESG Compliance & Long-Term Industrial Resilience
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) frameworks are now central to infrastructure investment decisions. Investors and stakeholders increasingly evaluate projects based on sustainability performance, carbon management, and social impact.
By adopting green infrastructure practices, companies strengthen investor confidence and improve regulatory compliance. Sustainable projects are more resilient to future environmental regulations and climate-related risks.
Aligning infrastructure development with ESG principles ensures that industrial expansion does not compromise environmental integrity or community well-being.

The Future of Sustainable Infrastructure in India
India’s path toward becoming a global manufacturing and logistics hub depends on building infrastructure that is both robust and environmentally responsible. Continued rail electrification, renewable energy adoption, multimodal integration, and green construction standards will define the next phase of infrastructure growth.
As industrial output rises, sustainable logistics solutions will become critical to balancing economic expansion with environmental conservation. Infrastructure innovation must therefore focus on efficiency, reduced emissions, and intelligent resource management.
Developers who integrate sustainability into every phase—from planning and design to construction and operation—will lead India’s transition toward a greener industrial future.
Conclusion
Sustainable infrastructure innovation is reshaping the way India approaches industrial growth. By aligning railway development, logistics integration, renewable energy adoption, and green construction practices, the nation is building an infrastructure ecosystem that supports both economic progress and environmental responsibility.
For infrastructure leaders, sustainability is not a constraint—it is a competitive advantage. Forward-thinking organizations that prioritize eco-friendly engineering and ESG compliance will play a central role in strengthening India’s industrial backbone while safeguarding its environmental future.
ESG Compliance & Long-Term Industrial Resilience
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) frameworks are now central to infrastructure investment decisions. Investors and stakeholders increasingly evaluate projects based on sustainability performance, carbon management, and social impact.
By adopting green infrastructure practices, companies strengthen investor confidence and improve regulatory compliance. Sustainable projects are more resilient to future environmental regulations and climate-related risks.
Aligning infrastructure development with ESG principles ensures that industrial expansion does not compromise environmental integrity or community well-being.

The Future of Sustainable Infrastructure in India
India’s path toward becoming a global manufacturing and logistics hub depends on building infrastructure that is both robust and environmentally responsible. Continued rail electrification, renewable energy adoption, multimodal integration, and green construction standards will define the next phase of infrastructure growth.
As industrial output rises, sustainable logistics solutions will become critical to balancing economic expansion with environmental conservation. Infrastructure innovation must therefore focus on efficiency, reduced emissions, and intelligent resource management.
Developers who integrate sustainability into every phase—from planning and design to construction and operation—will lead India’s transition toward a greener industrial future.
Conclusion
Sustainable infrastructure innovation is reshaping the way India approaches industrial growth. By aligning railway development, logistics integration, renewable energy adoption, and green construction practices, the nation is building an infrastructure ecosystem that supports both economic progress and environmental responsibility.
For infrastructure leaders, sustainability is not a constraint—it is a competitive advantage. Forward-thinking organizations that prioritize eco-friendly engineering and ESG compliance will play a central role in strengthening India’s industrial backbone while safeguarding its environmental future.
OUR LATEST NEWS
OUR LATEST NEWS
OUR LATEST NEWS




